[ad_1]
SEL is a common term in education, and the ideas and methods have been around for decades. But what exactly is social-emotional learning, and why does it matter? Here’s an overview for educators and parents.
What is social-emotional learning?

Source: PenPal Schools
Social-emotional learning, also called socio-emotional learning and SEL, encompasses the so-called “soft skills” of daily life. It teaches kids to manage their emotions, communicate with others, make smart choices, and more. Kids pick up some SEL skills naturally as they grow, but teaching them directly ensures every child has the opportunity to build these vital qualities.
The SEL movement began in the 1960s, when researchers at the Yale School of Medicine’s Child Study Center sought to improve the educational experience for low-income minority children. They found that by encouraging students’ social and emotional growth, they could also improve their academic outcomes. In the following decades, educators embraced the concept of SEL, and it’s a regular part of many curriculum programs today.
Discover more about the history of SEL here.
What are social-emotional skills?
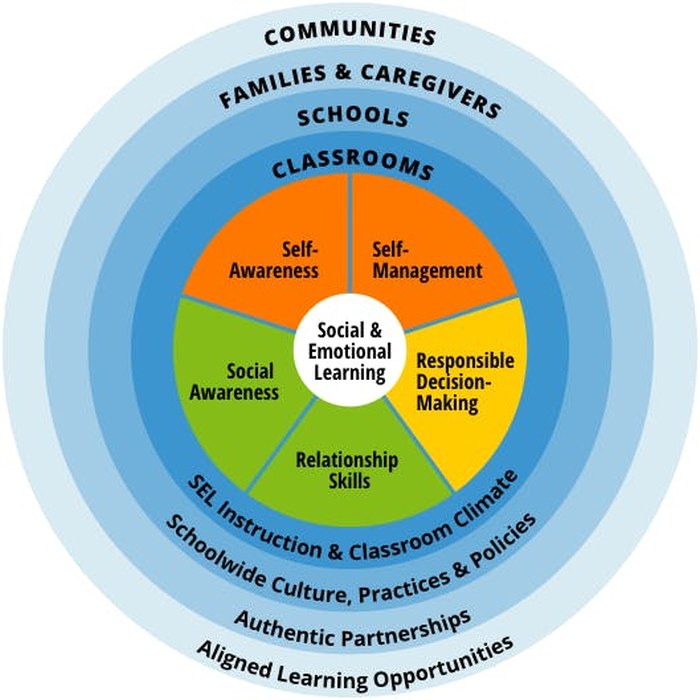
Source: CASEL
In the mid-1990s, the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) brought the term “social-emotional learning” to the forefront. They established a set of five foundational SEL competencies every child should learn, as presented in the CASEL Wheel.
Self-Awareness
This SEL skill is about recognizing your own emotions, thoughts, and values. Students learn to recognize their personal strengths and challenges, and develop a growth mindset. They examine their prejudices and biases, reflect on their own role in society, and develop a sense of purpose.
Learn more about SEL self-awareness skills here.
Self-Management
In addition to identifying their emotions, students must learn to manage them as well. They develop the skills to behave appropriately in various situations, like impulse-control and self-discipline. Kids learn time management and how to handle stress and anxiety. They also discover the best ways to motivate themselves to achieve goals they’ve set.
Explore SEL self-management skills here.
Responsible Decision-Making
Through SEL activities, students learn how to assess a situation and make smart decisions. They examine ethical implications, learn to separate fact from opinion, and develop strong critical thinking skills. Students also consider the potential impacts of their choices on themselves and others.
Find out more about SEL responsible decision-making skills here.
Relationship Skills
This skill is all about how students relate to others, from family and friends to people in the global community. Kids learn to communicate clearly, listen actively, and work collaboratively. They discover constructive ways to resolve conflicts and solve problems. Students also develop an understanding of what a healthy relationship looks like and learn to resist negative social pressure.
Learn about SEL relationship skills here.
Social Awareness
As students develop social awareness, they recognize that others have different backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives than their own. They develop a sense of empathy and compassion and learn to embrace others’ strengths. Kids learn that social norms vary across cultures and situations, and they explore the ideas of justice and injustice.
Discover more about SEL social-awareness skills here.
Why is SEL so important?
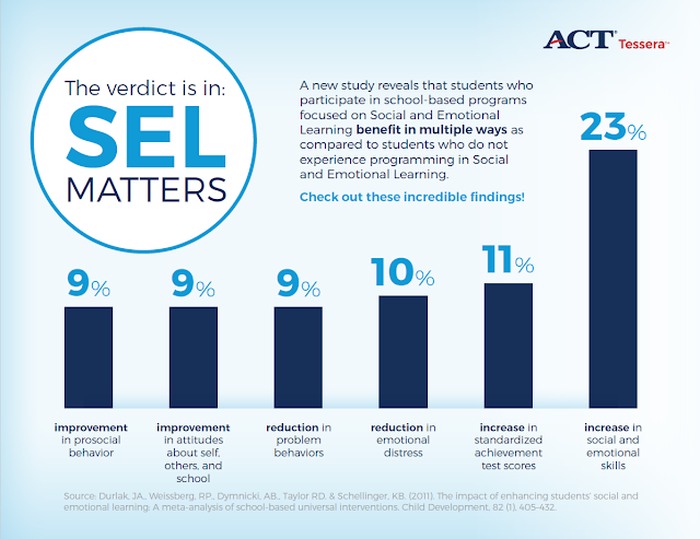
Source: ACT
You might have heard about backlash against SEL in schools. However, study after study confirms it: SEL improves the educational experience and academic outcomes for kids. It reduces bullying, increases resiliency, and provides kids with coping skills for dealing with anxiety and depression. What’s more, the benefits of active social-emotional learning last: Follow-up studies show students are more likely to graduate high school, go on to secondary education, and maintain stable, full-time employment.
Review a variety of SEL studies and results here.
In recent years, though, there’s been some pushback against including SEL in core standards and prescribed learning curriculum programs. Despite the overwhelming evidence in its favor, some school districts and parent groups have denounced SEL. They want to remove it from the curriculum and place a higher emphasis on academic skills and test scores.
Experts, though, continue to stress that SEL skills and academic outcomes go hand-in-hand. When you remove social-emotional learning from the curriculum, students don’t develop the skills they need to deal with daily life and relationships. This makes it harder for them to focus on school and academics, and their performance drops.
Explore the connection between mental health and academic success here.
How do you teach social-emotional skills?

Source: Pathway 2 Success
CASEL encourages schools and teachers to use effective evidence-based SEL programs in their classrooms. These programs should meet the SAFE criteria:
- Sequenced: The program should include connected, coordinated activities that build SEL skills over time.
- Active: Students should have the chance to actively participate, practicing new skills on a regular basis.
- Focused: Educators must make time in the curriculum to give SEL skills the attention they deserve.
- Explicit: The program should target specific social and emotional skills, with concrete lessons, exercises, and activities to support learning.
If your school has a specific SEL curriculum program, take advantage of the resources it supplies. If not, talk with your administrators about exploring available programs and implementing one in your school. Studies show that social-emotional learning works best when it’s supported by the wider school, district, and community.
Find out how to choose an SEL program for your school or district here.
SEL Activities for the Classroom
Even if your school doesn’t have an SEL curriculum program, you can still foster social-emotional skills in your classroom. Here are some resources to get you started (plus, find lots more here!).
Have more questions about social-emotional learning in the classroom? Come talk it over with other educators in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, 20 Growth Mindset Activities To Inspire Confidence in Kids.
[ad_2]
Source link
